Net income, often referred to as the bottom line, is a crucial metric in evaluating a company’s financial performance. It represents the amount of money a company has earned after deducting all expenses, taxes, interest, and other costs from its total revenue.
This financial figure serves as a key indicator of a company’s profitability and is a cornerstone in financial analysis, providing valuable insights into the company’s financial health and operational efficiency.To understand net income fully, it’s essential to grasp its calculation process.
Net income is calculated by subtracting total expenses from total revenue. Total revenue encompasses all the income earned by the company from its primary business activities, such as sales of goods or services. On the other hand, total expenses encompass all costs incurred by the company in generating revenue, including operating expenses, cost of goods sold, taxes, interest expenses, and any other financial obligations.
Positive net income indicates that a company’s revenue exceeds its expenses, resulting in profitability. It demonstrates the company’s ability to generate profits from its operations and indicates financial stability and growth potential.
Conversely, negative net income suggests that the company’s expenses surpass its revenue, indicating financial challenges or inefficiencies that require attention.The importance of net income in financial analysis cannot be overstated. It serves multiple critical functions in assessing a company’s financial performance and viability.
Firstly, net income provides a clear indication of the company’s profitability over a specified period, such as a fiscal quarter or year. Investors, analysts, and stakeholders rely on this metric to gauge the company’s ability to generate returns on investment and sustain profitability.
Positive net income instills confidence among investors, indicating that the company is effectively managing its resources and generating profits from its core business activities. It reflects positively on the company’s management team, operational efficiency, and strategic decision-making.
Conversely, negative net income may raise concerns among stakeholders and prompt further scrutiny of the company’s financial health and performance. Moreover, net income serves as a key metric for evaluating financial performance and making informed investment decisions.
Investors analyze trends in net income over time to assess the company’s growth trajectory, profitability ratios, and overall financial stability. They use this information to identify investment opportunities, mitigate risks, and allocate their capital effectively.
In addition to its role in financial analysis, net income plays a crucial role in financial planning and decision-making within the company. Management relies on net income to evaluate the effectiveness of cost-control measures, revenue-generating initiatives, and overall business performance.
By analyzing trends in net income, management can identify areas for improvement, optimize resource allocation, and formulate strategic plans to enhance profitability and sustainability. Furthermore, net income is a key component of financial statements, such as the income statement.
Financial statements provide a comprehensive overview of a company’s financial performance, liquidity, and solvency. Net income serves as a cornerstone of these statements, offering valuable insights into the company’s earnings and profitability ratios, such as return on investment (ROI) and earnings per share (EPS).
Read Also: The Ultimate Guide to PayPal Goods
How to Calculate The Net Income of A Company

Calculating the net income of a company is a fundamental aspect of financial analysis, providing valuable insights into its profitability and financial performance. In this beginner’s guide, we’ll walk through the steps involved in calculating net income, along with an illustrative example to demonstrate the process.
Step 1: Gather Financial Information
Before calculating net income, gather the necessary financial information from the company’s income statement. This includes total revenue, total expenses, taxes, interest expenses, and any other relevant costs.
Step 2: Calculate Gross Revenue
The first step in calculating net income is determining the company’s gross revenue. Gross revenue represents the total income generated by the company from its primary business activities, such as sales of goods or services. This figure is typically reported at the top of the income statement.
Step 3: Deduct Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Next, deduct the cost of goods sold (COGS) from the gross revenue to arrive at the gross profit. COGS represents the direct costs associated with producing or acquiring the goods sold by the company. It includes expenses such as raw materials, labor, and manufacturing overhead.
Step 4: Subtract Operating Expenses
After calculating gross profit, subtract operating expenses from the gross profit to determine the operating income. Operating expenses include costs incurred in the day-to-day operations of the business, such as salaries, rent, utilities, marketing expenses, and depreciation.
Step 5: Account for Non-Operating Items
In addition to operating expenses, consider any non-operating items that may impact the company’s income statement. These may include interest expenses, taxes, gains or losses from investments, and other one-time or non-recurring expenses or income.
Step 6: Calculate Net Income
Finally, subtract taxes, interest expenses, and any other non-operating expenses from the operating income to arrive at the net income. Net income, also known as net profit or the bottom line, represents the final amount of income earned by the company after deducting all expenses and taxes.
Example: Calculating Net Income
Let’s consider an example to illustrate the calculation of net income for a fictional company, ABC Corporation. ABC Corporation’s income statement for the fiscal year ending December 31, 20XX, is as follows:
- Gross Revenue: $1,000,000
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): $400,000
- Operating Expenses: $300,000
- Interest Expenses: $50,000
- Taxes: $30,000
Using the information provided, we can calculate ABC Corporation’s net income as follows:
- Gross Profit = Gross Revenue – COGS
Gross Profit = $1,000,000 – $400,000
Gross Profit = $600,000 - Operating Income = Gross Profit – Operating Expenses
Operating Income = $600,000 – $300,000
Operating Income = $300,000 - Net Income = Operating Income – Interest Expenses – Taxes
Net Income = $300,000 – $50,000 – $30,000
Net Income = $220,000
Therefore, ABC Corporation’s net income for the fiscal year ending December 31, 20XX, is $220,000.
The Benefit of Calculating The Net Income of A Company
Calculating the net income of a company offers numerous benefits for stakeholders, investors, management, and other interested parties. Understanding and analyzing net income provides valuable insights into a company’s financial health, performance, and overall profitability. Below are some key benefits of calculating the net income of a company:
1. Measure of Profitability: Net income serves as a primary measure of a company’s profitability. It indicates the amount of money a company has earned after deducting all expenses, taxes, interest, and other costs from its total revenue. Positive net income indicates that the company is generating profits from its operations, while negative net income signals financial challenges or inefficiencies.
2. Evaluation of Financial Performance: Net income is a critical metric for evaluating a company’s financial performance over a specific period, such as a fiscal quarter or year. By comparing net income to previous periods or industry benchmarks, investors and analysts can assess the company’s growth trajectory, profitability trends, and overall financial health.
3. Decision-Making Tool: Net income provides valuable information for decision-making within the company. Management relies on net income to assess the effectiveness of business strategies, resource allocation, and cost-control measures. By analyzing trends in net income and identifying factors that contribute to fluctuations, management can make informed decisions to optimize profitability and drive sustainable growth.
4. Investor Confidence: Positive net income instills confidence among investors and stakeholders, indicating that the company is generating returns on their investment. Investors use net income as a key factor in evaluating the attractiveness of a company’s stock and its potential for long-term growth and financial stability. Consistently strong net income figures may attract new investors and support a higher stock price.
5. Basis for Dividend Payments: Net income plays a crucial role in determining a company’s ability to pay dividends to its shareholders. Companies with positive net income often distribute a portion of their earnings to shareholders in the form of dividends. Investors rely on consistent dividend payments as a source of income and as a sign of financial strength and shareholder value.
6. Benchmarking and Comparison: Net income serves as a benchmark for comparing the financial performance of different companies within the same industry or sector. Investors and analysts use metrics such as net income margin (net income divided by total revenue) to assess a company’s profitability relative to its peers. This comparative analysis helps identify industry leaders, evaluate competitive positioning, and make informed investment decisions.
7. Compliance and Reporting Requirements: Net income is a key component of financial statements, such as the income statement, which companies are required to prepare and disclose to regulatory authorities and stakeholders. Accurate reporting of net income ensures compliance with accounting standards and regulations, providing transparency and accountability to investors and the public.
8. Indicator of Financial Health: Net income serves as an indicator of a company’s overall financial health and viability. Positive net income demonstrates that the company’s revenue exceeds its expenses, indicating a sustainable business model and effective management of financial resources. Conversely, negative net income may raise concerns about the company’s ability to cover its obligations and sustain its operations in the long run.
9. Strategic Planning and Forecasting: Net income provides valuable data for strategic planning and forecasting future financial performance. By analyzing historical net income trends and projecting future earnings potential, companies can develop strategic initiatives, allocate resources effectively, and set realistic financial goals. This proactive approach to financial management enhances the company’s competitiveness and resilience in the marketplace.
10. Stakeholder Communication: Net income serves as a key metric for communicating with stakeholders, including investors, creditors, employees, and regulators. Companies use net income figures to provide updates on financial performance, highlight achievements, and address concerns or challenges. Clear and transparent communication about net income fosters trust and confidence among stakeholders, strengthening relationships and enhancing the company’s reputation.
Read Also: Digital Marketing: A Step-By-Step Complete Guide
Reasons Why Calculating The Net Income is Important to The Growth of Every Business
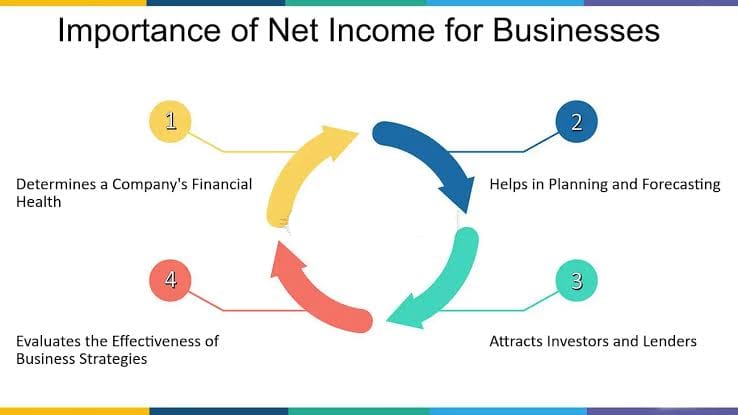
Calculating net income is crucial to the growth and success of every business, regardless of its size, industry, or stage of development. Net income serves as a key indicator of a company’s financial health, profitability, and overall performance. By understanding and analyzing net income, businesses can make informed decisions, identify opportunities for improvement, and chart a path toward sustainable growth.
1. Measure of Financial Performance: Net income serves as a primary measure of a company’s financial performance. It indicates the profitability of the business by showing how much revenue is left after deducting all expenses. Positive net income demonstrates that the company’s operations are generating profits, while negative net income signals potential financial challenges that need to be addressed.
2. Evaluation of Profitability: Calculating net income allows businesses to assess their profitability over a specific period, such as a fiscal quarter or year. By comparing net income to previous periods or industry benchmarks, businesses can gauge their performance and identify trends. Consistently increasing net income is often a sign of effective management, operational efficiency, and successful business strategies.
3. Financial Planning and Budgeting: Net income plays a critical role in financial planning and budgeting processes. By accurately forecasting net income based on expected revenue and expenses, businesses can set realistic financial goals and allocate resources effectively. Understanding projected net income helps businesses make informed decisions about investments, expenditures, and growth initiatives.
4. Resource Allocation: Calculating net income helps businesses allocate resources effectively to support growth and expansion efforts. By analyzing profitability metrics, such as net income margin (net income divided by total revenue), businesses can identify areas where resources are being underutilized or where investments may yield the highest returns.
5. Investment Attractiveness: Positive net income enhances a business’s attractiveness to investors and creditors. Investors use net income as a key metric to assess the financial health and performance of a company.
A track record of consistent profitability can attract new investors, increase shareholder confidence, and support a higher valuation for the business. Positive net income also improves a company’s creditworthiness, making it easier to secure financing for growth initiatives.
6. Strategic Decision-Making: Net income provides valuable insights for strategic decision-making within the business. By analyzing net income trends and identifying factors that contribute to fluctuations, businesses can make informed decisions about pricing strategies, product development, market expansion, and other growth initiatives.
7. Performance Evaluation: Net income serves as a benchmark for evaluating the performance of different business units, departments, or product lines within the company. By comparing net income across various segments of the business, management can identify areas of strength and weakness and allocate resources accordingly.
8. Compliance and Reporting: Calculating net income ensures compliance with accounting standards and regulatory requirements. Businesses are required to prepare and disclose financial statements, including income statements, to regulatory authorities, investors, and other stakeholders. Accurate reporting of net income provides transparency and accountability, building trust with stakeholders and enhancing the company’s reputation.
9. Business Valuation: Net income is a key factor in valuing a business for mergers, acquisitions, or sale transactions. Potential buyers or investors often use net income multiples, such as price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios, to assess the value of a business relative to its earnings. A strong track record of positive net income can increase the perceived value of the business and attract favorable offers from potential buyers.
10. Long-Term Sustainability: Ultimately, calculating net income is essential for ensuring the long-term sustainability and success of a business. Positive net income indicates that the business is generating profits, reinvesting in growth opportunities, and creating value for shareholders, employees, and other stakeholders.
In conclusion, calculating net income is crucial to the growth and success of every business. Net income serves as a key measure of financial performance, profitability, and operational efficiency. By understanding and analyzing net income, businesses can make informed decisions, allocate resources effectively, attract investment, and chart a path toward sustainable growth and prosperity.
As businesses navigate evolving market conditions and pursue growth opportunities, the importance of calculating net income remains paramount in driving strategic decision-making and achieving long-term success.
Read Also: 5 Ways to Make Money Online this Year






